Dear Atlasser,
COVID-19: The Atlas team reminds all atlassers to be aware of the latest COVID-19 conditions in Ontario. Please follow all public health guidelines and restrictions, and check for updates frequently. Information on the latest conditions and public health guidance can be found on the Government of Ontario website. Follow the links to the most current situation in the province.
In 2022 and beyond, if COVID protocols and restrictions permit it, we will be focusing a lot of effort on getting atlassers back into northern Ontario, especially into remote areas. Given the lack of data collection in the remote north in 2021, we have some catching up to do.
One of our main priorities is to repeat atlas work done in Atlas-2, from 2001-05, covering the same squares and even a lot of the same point counts. This will primarily involve teams of four people canoeing northern rivers, especially those that pass through the Hudson Bay Lowlands. We are working to subsidize the cost of these trips.
The table below and the map provided here both show nine of the trips we are hoping to run in 2022 and beyond. A more comprehensive list will be available on the Atlas-3 website later this fall. All of the 100-kilometre blocks in northern Ontario must be adequately covered by the end of 2025.
For the nine trips listed here, at least two people in each team of four need to be expert birders capable of doing point counts in remote northern Ontario. And all four need to be experienced campers and canoeists able to work safely in remote wilderness conditions. The trips vary in length from 10 to 17 days on the river, plus time getting to and from the north. Trips will run between mid-June and early July to be at the peak of breeding bird activity.
If you are interested in participating in any of these trips for Atlas-3 — or you have other remote atlassing trips in mind — please visit our website and complete a remote northern atlassing application form providing information about yourself and a trip you would like to do. We will get back in touch with you with the goal of getting as many trips as possible going for 2022 and beyond. We will soon be posting a Northern Atlassing Manual to give you a more complete idea of what northern atlassing entails.
These trips provide a rare opportunity to experience and contribute to the conservation of Ontario’s amazing wilderness. We hope that folks with the right skills will join us for an extraordinary experience and make a valuable contribution to the Atlas project.
Remote Northern Canoe trips
Nine suggested trips are shown on the map and in the table below. If you are interested, please fill out an application form on the website asap.
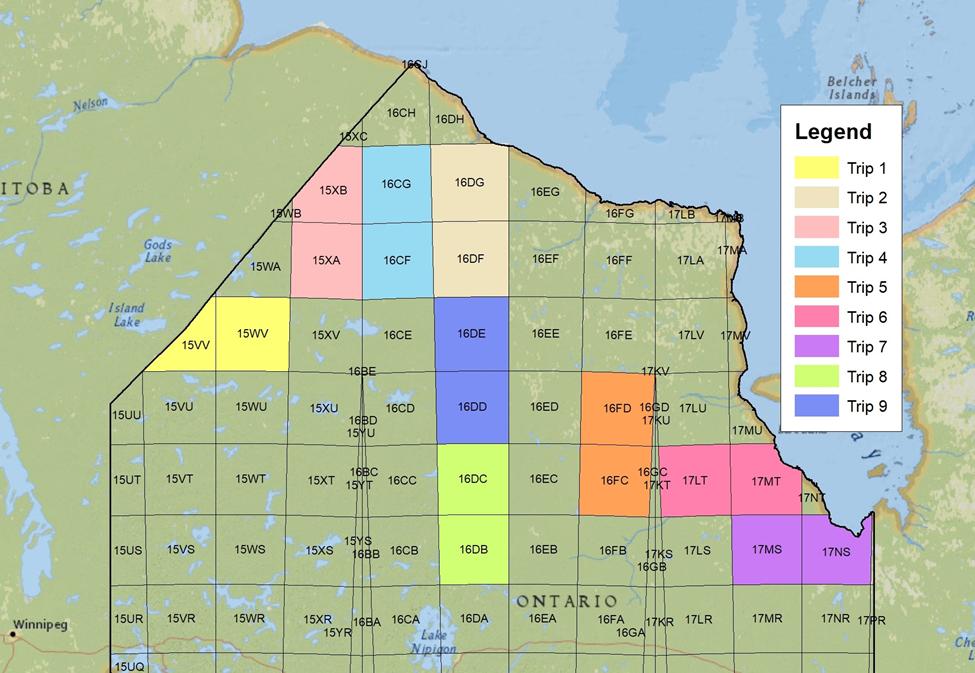
|
Trip #
|
Target Blocks |
Location |
Suggested Itinerary (based on Atlas-2) |
Length of trip (canoe portion) |
|
1
|
15VV, 15WV |
Opasquia Provincial Park |
Drive to Vermillion Bay, float-plane to Opasquia Provincial park and back, then drive home. |
12 days |
|
2
|
16DF, 16DG |
Fawn and Severn Rivers |
Drive to Sioux Lookout, float-plane to Fawn River, canoe down Fawn River, then Severn River, commercial flight from Fort Severn to Sioux Lookout, drive home. |
17 days |
|
3
|
15XA, 15XB |
Sachigo River (Upper) |
Drive to Nakina, float-plane to upper Sachigo River, canoe downstream, float-plane back out, then drive home. |
15 days |
|
4
|
16CF, 16CG
|
Sachigo River (Lower)
|
This trip will be paired with the upper Sachigo Trip. The pick-up flight for the upper trip will bring in the crew for the lower Sachigo trip. |
12 days |
|
5
|
16FC, 16FD |
Missisa Lake and River |
Drive to Hearst, float-plane to Missisa Lake, paddle to Attawapiskat River, float-plane to Hearst, drive home. |
10 days |
|
6
|
17LT, 17MT |
Albany River |
Drive to Hearst, float-plane to Albany River, paddle 150 km to Fort Albany, commercial flight to Moosonee, travel to Hearst, drive home. |
15 days |
|
7
|
17MS, 17NS |
Moose River |
Drive to Cochrane, train to Moose River, paddle to Moosonee, train back to Cochrane, then drive home. |
10 days |
|
8
|
16DB, 16DC |
Upper Albany River |
Drive to Nakina, float-plane to Fort Hope, paddle downstream, float-plane from Washi Lake to Nakina, then drive home. |
10 days |
|
9
|
16DD, 16DE |
Upper Winisk River |
Travel to Thunder Bay, commercial flight to Webequie, paddle the upper Winisk River, float-plane to Hearst, travel home. May link this trip to a lower Winisk trip. |
15 days |
Sappy Hour, November 23, 2021: Atlassing in the remote north
Mark your calendar now. To help get you in the mood for northern adventure, we are devoting the November 23 Sappy Hour to Atlassing in the remote north. Special guest Michael Runtz will provide a 20 minute presentation about his atlassing trip down the Muketei River in the Hudson Bay Lowlands during Atlas-2; Mike Cadman, Mike Burrell and Adam Timpf will provide general information and answer questions about our plans for northern atlassing; Emily Rondel will keep us all in line; and Kaelyn will keep the broadcast running smoothly.
The event will take place on Zoom webinar (register using the link – here) and will also be streamed to Facebook Live (www.facebook.com/ONBreedingBirdAtlas/live). The event will be recorded for those who cannot attend either on Facebook or Zoom and will be available on our YouTube channel.
Square-bashing coming soon!
We are delighted to announce that plans are underway for our first “square-bash” events for Atlas-3 (Covid safety precautions/restrictions permitting). Square-bashes are fun and productive activities focused on filling gaps in atlas coverage. Both are planned for beautiful provincial parks on the Canadian Shield in June of 2022, in areas rich with warblers, thrushes and other “central” Ontario species. At each location, five campsites (maximum 6 people per site) have been set aside for atlassers with no charge for camping. At least some of the sites will be electrical.
The first is to be at Grundy Provincial Park, north of Parry Sound, from Friday, June 10th to Wednesday, June 15th, 2022. The second is at Mikisew Provincial Park, near South River, from Friday, June 17th to Wednesday, June 22nd, 2022. You could come for the whole 5 days or just part of that time. Our goal is to provide adequate coverage for as many squares as possible in and around each park.
If you are interested in taking in either of these events, please email Kaelyn at atlas@birdsontario.org, telling us which location, what dates work for you, how many people are in your party and whether or not you can do point counts. Please do not contact the parks about these square-bash events as all arrangements are being made through the atlas office.
Hoping you can join us! Thanks to Ontario Parks for making these opportunities available.
Backcountry atlassers wanted in Algonquin
Completing >20 hours of atlassing and >25 point counts during the core period (24 May to 5 July) for the many squares in the interior of Algonquin Provincial Park is very challenging. But for experienced atlassers who are avid canoe campers or backpackers, this area offers beautiful landscapes and excellent birding.
We’re keen to recruit experienced campers to do atlassing in backcountry squares in Algonquin Park that so far have few hours logged during the core period (i.e., <10 hours). If you have a backcountry trip in mind where you can complete at least 20 hours of atlassing in squares that still need hours or you can complete at least 25 in-person or digital point counts in squares that still need them, then we would very much like to hear from you.
If your proposed canoeing or backpacking atlas trip is approved by the Region 27 coordinators and Algonquin Park staff, then your backcountry camping permits will be provided free of charge. To submit a proposed trip plan for review and potential approval, please complete the application form. Please be prepared to provide the number of hours and the number of in-person or digital point counts, if any, you expect to complete in each square you plan to visit during the core period.
Owling in November
If you check the Safe Date charts, you will notice that it is safe to report breeding evidence for Eastern Screech-Owl in November and December, and for Great Horned Owl in December in southern Ontario. Both species are quite vocal at this time of year as they advertise their territories and seek mates. Although November is in the shoulder season for Great Horned Owls (when some are starting breeding behaviours and some are still dispersing), calling birds can be counted as “S” for singing and “T” for Territory. So, to clarify, calling Screech-Owls and Great Horned Owls in November and December can be counted as breeding evidence for the Atlas. Great Horned Owls in November that are not calling should not be given breeding evidence.
Atlasser chip notes
Atlassing Adventures in Wabakimi Summer 2021, by Mhairi McFarlane
Having taken up canoeing on, appropriately, Canada Day in just 2020, the next obvious step was to embark on an 18-day, 300-km wilderness trip in 2021. Although this sounds crazy, we’ve been privileged to have done plenty of wilderness hiking in various parts of the world, and had done two white water canoe training courses and a river rescue course, so we were more prepared than it sounds. It seemed obvious that this was a great opportunity to contribute to Atlas-3. With lots of unknowns around COVID-19 restrictions, there were unlikely to be any organized trips to the north in 2021. We gritted our teeth about feeding the bugs and arranged our dates to coincide with breeding bird season. Two days of driving later, we arrived at Armstrong and were dropped off by an outfitter at the roadside at the south end of Caribou Lake, on June 21, 2021. This was the start of a 300 km adventure that would take us across Wabakimi Provincial Park, down the Misehkow River and along the Albany River to Miminiska Lake, where our outfitter would pick us up in a float plane on July 8th. We borrowed two Acoustic Recording Units (ARU) and a handheld recording device and I received a great training session from Rich Russell, a wildlife biologist at the Canadian Wildlife Service, over zoom before we left.
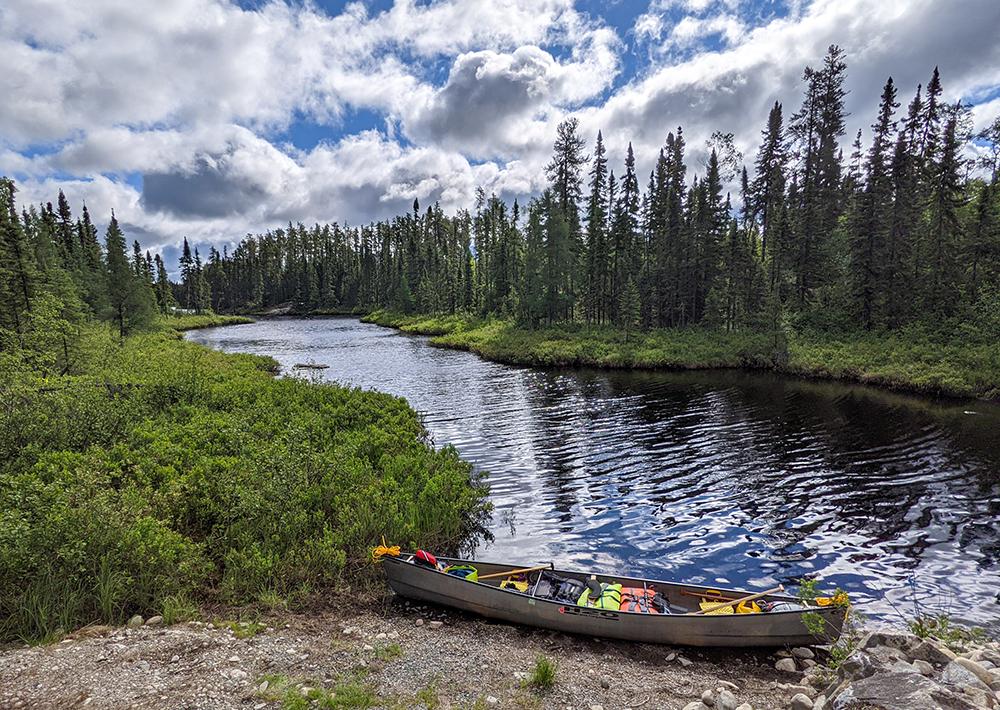

All packed up and ready to go: our put-in at the start of our 300 km, 18 day adventure. Caribou Lake Road, June 21, 2021 ©Mhairi McFarlane
I downloaded the Atlas squares we would paddle through to the Gaia GPS app, and attempted to collect data in as many as possible. We had some pretty tough conditions, including headwinds for the first week, which lost us some time, then some rather epic portage clearing, so we had a lot less time and energy to collect data than I’d hoped. It turns out that rolling into camp between 6 and 9 pm is not conducive to early morning starts, so I only managed 2 in-person point counts! We managed to get either one or both of the ARUs out on 13 nights, for a total of 19 recording sessions. Combined with around 135 daytime eBird checklists which I ported over to the atlas, it was pleasing to be able to add some data for quite a few pretty remote squares.
These figures show the general location of our canoe route, north of Lake Nipigon, and a more detailed view of the squares we passed through along the way.
Some species which dominated the soundscape throughout include Northern Waterthrush and White-throated Sparrows, while Tennessee Warblers split our ears along the shrubby banks of the Misehkow in particular. It was a new experience for me to be dive-bombed by Greater Yellowlegs – despite our best efforts to avoid disturbing the many pairs we encountered. The Misehkow area also proved to be quite the Common Goldeneye factory, with the occasional Mallard and American Black Duck too. We came across one probable and one confirmed breeding Trumpeter Swan. One highlight was a flock of 14 American White Pelicans on our very last morning on Miminiska Lake! We came across quite a few sets of Boreal Chickadees, and had several fun encounters with Canada Jays with young of the year in tow.
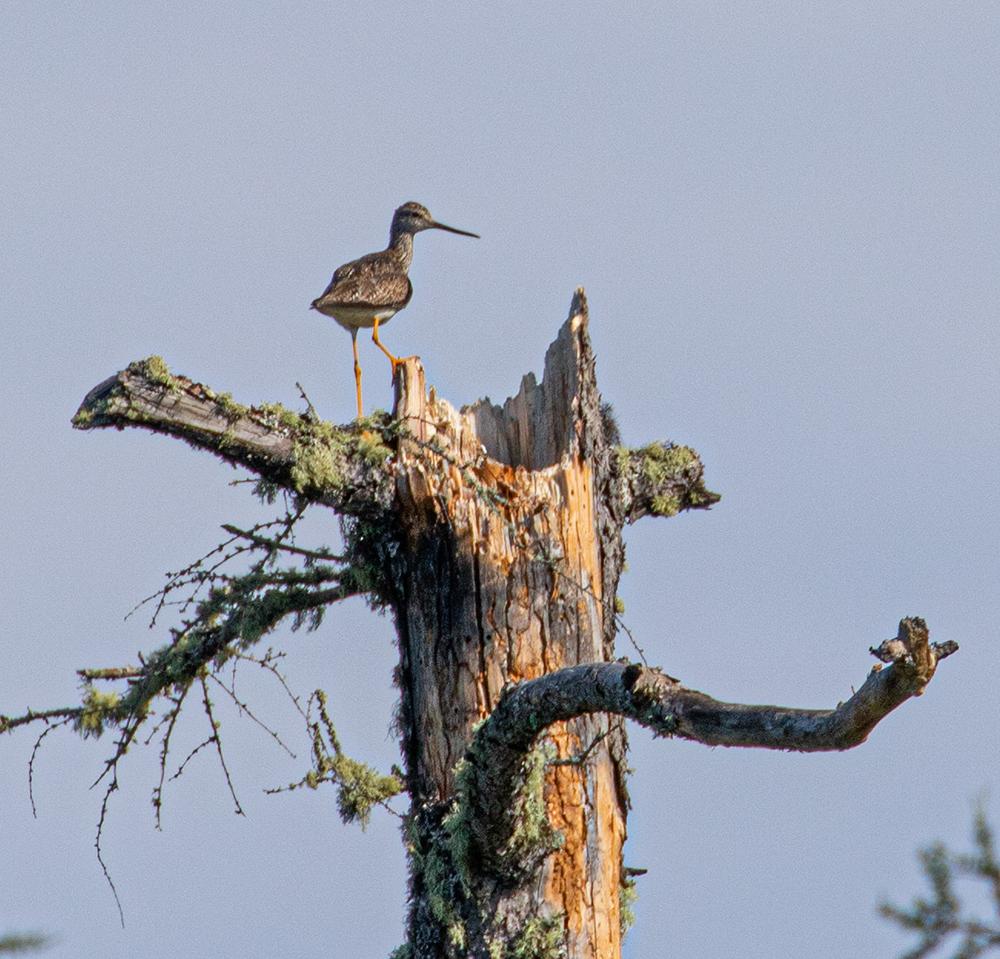

I always get a kick out of seeing shorebirds up trees! This was one of many very territorial Greater Yellowlegs we came across on the Albany River July 6, 2021 ©Mhairi McFarlane
We enjoyed some great non-bird experiences too of course: we almost lost count of how many American Black Bears and Moose we saw, but we were particularly excited to see Woodland Caribou on two occasions. Both were very distant groups of swimming adults with calves in tow.
In terms of gear, some items we were very grateful to have: “Eureka no-bug zone” bug shelter. Although the biting insects weren’t as bad as they can be, they certainly had their moments and this bug tarp provided some much needed relief during mealtimes. Although we relied on paper maps for navigation, having Gaia GPS app on our phones was very helpful for small-scale route finding, and making sure where the Atlas squares were. We also used our phones for eBird, iNaturalist, and photos, so we appreciated having a couple of battery packs and a “Big Blue” solar charger. Our canoe is an H2O Voyageur 17’, made of innegra-kevlar-epoxy (approximately 25 kg, 55 lbs). Despite low water levels and many associated knocks and scrapes, it performed extremely well on flatwater and rapids alike. It now has many, many battle scars, but no repairs required!
We did not see any other humans at all between day 2 and day 16, so it was a true wilderness experience. Despite the occasional hardships of this trip, I can’t wait to embark on another northern river adventure in 2022, building on what I learned this year and hopefully contributing more data from another part of Ontario’s stunning boreal landscape. You can read more technical details about our trip on the Friends of Wabakimi trip forum page here: https://www.wabakimi.org/trip-report-forum.html (look for “Little Caribou to Miminiska, June/July 2021”).
If you have an interesting discovery or fun story to share from your atlassing that you’d like to share, please send it to atlas@birdsontario.org
Until next time,
– The Atlas-3 Team
The Ontario Breeding Bird Atlas-3 thanks the following for their financial support:
| Environment and Climate Change Canada
TD Friends of the Environment Foundation
Vortex |
Natural Resource Solutions Inc.,
Hodgson Family Foundation
Baillie Fund |
RBC Foundation
Employment and Social Development Canada
(Canada Summer Jobs) |
The Ontario Breeding Bird Atlas-3 thanks the following for their in-kind support:
| Boreal Avian Modelling Project
Natural Resources Canada
Ontario Parks
Parks Canada |
Royal Ontario Museum
Sustainable Forestry Initiative
University of Alberta
Wild Birds Unlimited |
WildTrax
Ministry of Northern Development, Mines, Natural Resources and Forestry
|